Description
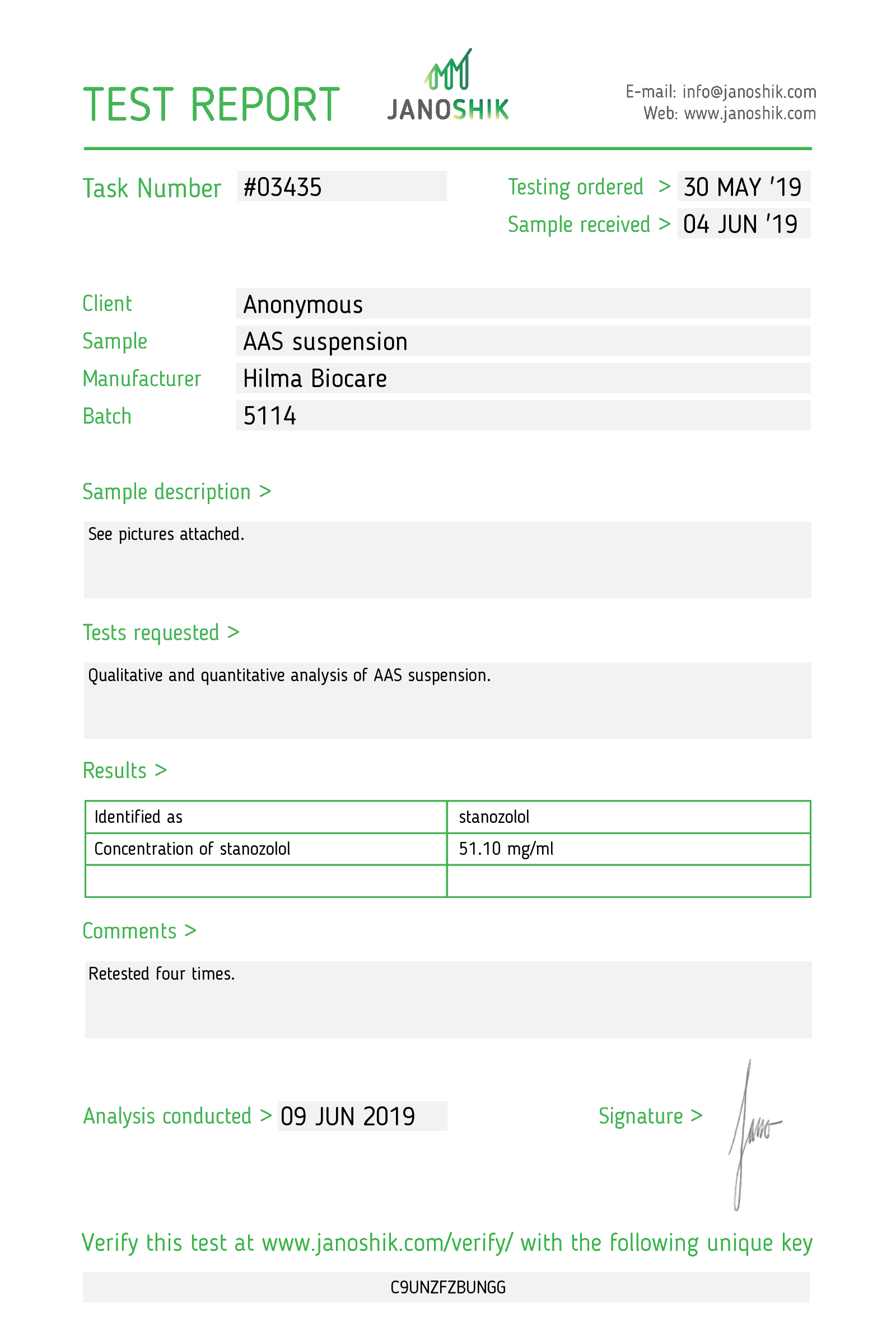
Stanozolol
Strength: 50 mg/ml
Molecular Formula: C21H32N2O
Molecular Weight: 328.49 g/mol
Active Ingredient: Stanozolol
CAS number: 10418-03-8
Dosage Form: Injectable, water base sterile solution
Route: Injection
Market Status: Prescription
Company: Hilma Biocare
DESCRIPTION
Stanozolol 50 is an aqueous suspension of the C17 a-alkylated steroid stanozolol, an oral
androgen derived from dihydro- testosterone. Stanozolol 50 acts on androgen receptors to
promote anabolism through increased nitrogen retention and protein synthesis in muscle
tissue. Stanozolol 50 is a strong anabolic substance with androgenic action. Stanozolol does
not convert to estrogen and therefore does not produce typical estrogen mediated side
effects such as water retention. While chemically identical to oral stanozolol, Stanozolol 50 is
injected IM eliminating the first pass of liver metabolism of its oral counterpart reducing
stress on the liver. Stanozolol reduces SHBG increasing free testosterone levels.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Anabolic steroids are synthetic derivatives of the natural steroid testosterone. Stanozolol has
been demonstrated to increase LDL and decrease HDL with serum lipid values Ta returning
to baseline after cessation of use. Hereditary angioedema (HAE) is an autosomal dominant
disorder caused by a deficient or nonfunctional C1 esterase inhibitor (C1 INH) and is
clinically characterized by episodes of swelling of the face, extremities, genitalia, bowel wall,
and upper respiratory tract. In small clinical studies, stanozolol was effective in controlling
the frequency and severity of attacks of angioedema and in increasing serum levels of C1
INH and C4. Stanozolol is not effective in stopping HAE attacks while they are underway.
The effect of stanozolol on increasing serum levels of C1 INH and C4 may be related to an
increase in protein anabolism.
INDICATIONS
Hereditary Angioedema: for prophylactic use to decrease frequency and severity of attacks
of angioedema. Muscle Anabolism: for adjunctive therapy in patients for weight gain
following severe muscular atrophy associated with extensive surgery, chronic infections,
long term hospitalization, or severe trauma. Corticosteroid Atrophy: to reduce muscle
wasting during prolonged corticosteroid use.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Not for use in female patients due to risk of virilization and fetal harm. Male patients with
known or suspected carcinoma of the breast, prostate, or testis. Patients with
hypercalcaemia as anabolic steroids may stimulate osteolytic bone resorption. Patients with
cardiovascular disorders, renal or hepatic impairment, epilepsy, migraines, or diabetes
mellitus. Nephrosis or the nephrotic phase of nephritis.
PRECAUTIONS
Anabolic steroids may cause suppression of clotting factors II, V, VII and X and an increase
in prothrombin time. Anabolic steroids may increase sensitivity to anticoagulants. Dosage of
anticoagulants may have to be decreased in order to maintain the prothrombin time at the
desired therapeutic level. Oral hypoglycemic dosage may need adjustment in diabetic
patients who receive anabolic steroids. Patients should be monitored for hepatotoxicity and
jaundicing.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hepatic: Cholestatic jaundice with rarely, hepatic necrosis and death. Hepatocellular
neoplasms and peliosis hepatis have been reported in association with long term androgenic anabolic steroid use. Reversible changes in liver function tests also occur including
increased bromsulpha- lein (BSP) retention and increases in serum bilirubin, glutamic
oxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), and alkaline phosphatase. Genitourinary System (post
pubertal men): inhibition of testicular functions, testicular atrophy, and oligospermia,
impotence, chronic priapism, epididymitis M and bladder irritability. Genitourinary System
(Women): Clitoral enlargement, menstrual irregularities. In both sexes: increased or
decreased libido. CNS: Habituation, excitation, insomnia, and depression. Hematologic:
Bleeding in patients on concomitant anticoagulant therapy. Hair: Hirsutism and male pattern
baldness in those genetically predisposed. oncie Other: Acne, oily skin, electrolytic retention,
reversible changes in serum lipids.
PATIENT MONITORING
Serum Cholesterol, HDL, LDL, TG. Hemoglobin and Hematocrit, Hepatic function tests –
AST/ALT. Prostatic specific antigen – PSA, Testosterone: total, free, and bioavailable.
Dihydrotestosterone & Estradiol. Male patients over 40 should undergo a digital rectal
examination and evaluate PSA prior to androgen use. Periodic evaluations of the prostate
should continue while on androgen therapy, especially in patients with difficulty in urination
or with changes in voiding habits.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Muscle anabolism: 50 – 100 mg injected IM every 2 days for a duration of 4 weeks. bem
Hereditary angioedema: as prescribed by physician. The use of anabolic steroids is
associated with serious adverse reactions. Such reactions are often dose dependent.
Physicians are urged to treat patients with the lowest possible effective dose.
PRESENTATION
Stanozolol 50 mg/ml, 10 single dose ampoules x 1 ml.
STORAGE
Store in a cool dry place between 15 – 25°C. Protect from light.